Exploring WebRTC Market Trends & Predictions for 2025
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) play a crucial role in this digital-first age, enabling seamless communication and integration between various software systems. Staying on top of the latest API trends is vital for businesses and developers to exploit new opportunities and deliver innovative solutions with fast time-to-market.
Empowering businesses with cutting-edge technology, Web Real-Time Communication (RTC) revolutionises customer engagement, enabling seamless and immersive real-time interactions. It offers various use cases, from simple web applications utilising camera or microphone capabilities to more sophisticated applications like video calling and screen sharing.
Table of Contents
- What is WebRTC?
- WebRTC market analysis
- WebRTC trends & predictions for 2025
- Unlocking the potential of WebRTC with Digital Samba
This article explores the latest WebRTC trends and predictions for 2025.
What is WebRTC?
It’s better to clear up what WebRTC is not. It is not a protocol! It is not a product. It is not an out-of-the-box solution.
WebRTC is a project.
Specifically, it’s a project or technology owned by Google that acts as a compatibility layer between clients (usually web browsers, but potentially discrete applications) so that the clients can communicate in real-time with one another.
You may, when working with coders, you may hear WebRTC referred to as a library. This is practically correct, but also kind of a misconception. A libwebrtc library contains a set of tools for implementing WebRTC that is officially released, but the library is not the project.
WebRTC technology enables real-time communication between web browsers or compatible applications without the need for additional plugins or software installations. It is open source and allows users to engage in various forms of communication, such as audio and video calls, live chat, and file sharing, directly from their web browsers. Visit our blog to explore WebRTC security best practices and considerations.
Following are a few use cases of WebRTC.
- Telehealth & remote monitoring: WebRTC enables video-enabled medical services ranging from virtual doctor visits to camera-assisted surgical technologies. With WebRTC powering telemedicine services, patients and doctors can use browser-based streaming to engage in low-latency video calls. Learn about encryption solutions for telehealth platforms here.
- Live commerce & shoppable video: WebRTC enables users to engage in real-time interactive sessions with sellers, explore products, and ask questions. Also, users can make purchases directly within the video stream, enhancing the online shopping experience.
- Online education: It facilitates interactive virtual classrooms and study sessions, enabling real-time audio and video communication between teachers and learners, enabling effective distant learning. To learn more about WebRTC for online education, visit our blog.
- Corporate communications: WebRTC empowers seamless corporate communications by enabling video conferences, webinars, and virtual meetings within organisations. It facilitates real-time collaboration and information sharing among stakeholders, regardless of their geographic locations.
A quick history of why WebRTC was invented
Clients such as web browsers can talk to web servers easily. That’s what they’re initially built to do. They visit web pages, take HTML CSS and maybe JavaScript from a server somewhere, and assemble that code into a web page that regular humans can look at with their eyeballs and interact with.
This is all that web browsers were all the way back to the advent of Netscape… Up until about 2009, when the internet really began to expand to include fundamentally different interactions than computers talking to web servers.
What if a client wants to talk to another client?
This is called peer-to-peer– and it’s also been around for ages. Many online chat programs were DCC (Direct Client to Client), and CTCP (Client to Client Protocol). BitTorrent is also peer-to-peer. Many early online game clients were strictly peer-to-peer, where clients would connect to other clients via IP addresses.
The problem with peer-to-peer applications was configuration. This was addressed by using discrete, pre-configured applications that handled these configuration problems. There was no widely adopted general way of establishing peer-to-peer connections for generic use around the web– and this is the problem that webRTC addressed.
The way WebRTC works
Let’s say we have two clients that want to establish a peer-to-peer connection. Well. First off… How do they know about each other? How do they discover each other on the internet?
This problem of clients discovering one another is called signalling. They signal each other, “Hey. I’m right here, and I am looking for a connection!” WebRTC itself does not handle any provisions for signalling; it hands that responsibility off to an application server. So both clients connect to a known server, and the server tells them what other clients are available to connect to.
When two clients want to connect, the signalling server acts as a middle-man. Both clients have to exchange configuration data in order to accept a peer-to-peer connection with one another. The technical term for this data is a Session Description Protocol (SDP) token. It basically tells the other connection things like window size, where to address peripherals like microphones, earphones, webcams, and other generic resources like video drivers or available video codecs that one client may have.
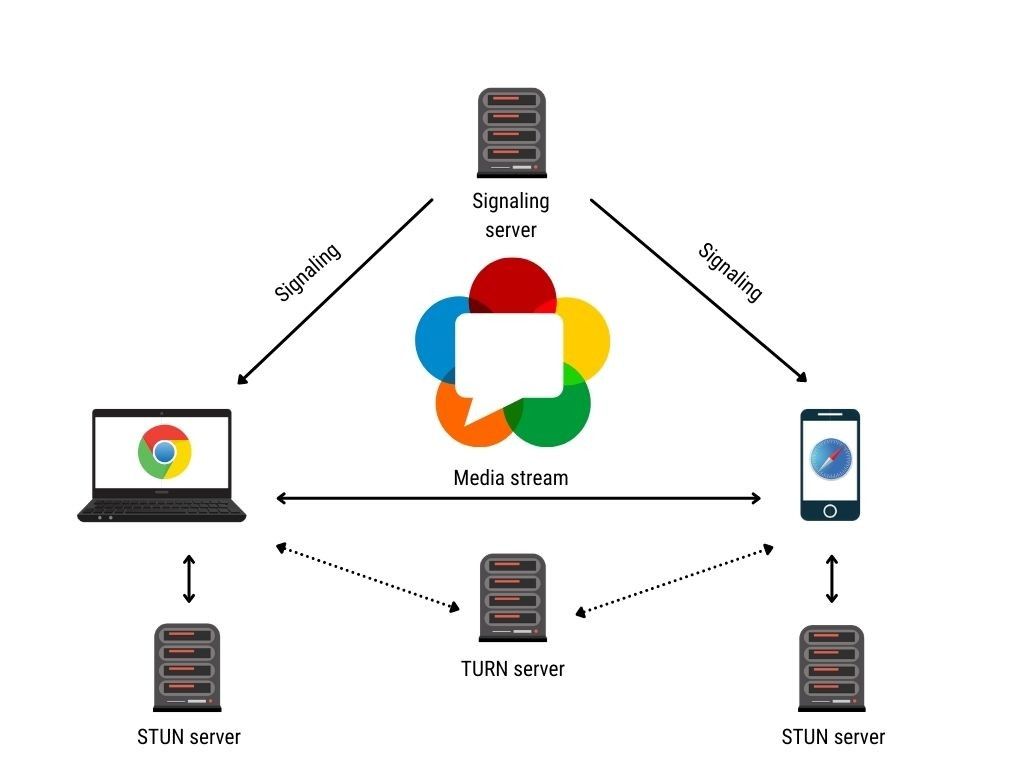
After the signalling server facilitates both clients exchanging their SDP tokens, it’s time for the clients to connect. The clients use ICE to implement a data stream to one another, but there are two main ways that the actual connection gets made between the clients, either by STUN or by TURN. You can think of ICE as a cable and STUN or TURN as the plugs that are on either end of that cable.
STUN servers are part of the clients themselves, which list their public network addresses for the other clients to connect to. Sometimes, firewalls and other network settings prevent these types of connections from being used directly. For that, there is the TURN type connection, which a trusted public server is connected to, which essentially bypasses the two clients from having to address or ‘plug into each other directly.

WebRTC connections go through the following operations to work:
- Signalling
- SDP token exchange through the signalling server
- Setting up STUN or TURN as their connection type
- Using ICE to establish a peer-to-peer data stream
If this sounds confusing; it’s because there is a lot of complexity that WebRTC has to handle in order to act as an effective compatibility layer across countless device types and configurations in hardware, software, and networking!
Is WebRTC good?
It depends. There are pros and cons to WebRTC. Here are some to consider:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Widely used by many apps |
Controlled by a single company (Google) |
|
Generally mature technology |
Can be complicated to develop with |
|
Stable and supported |
CPaaS may be better |
|
Contributed to and supported by Apple, Google, Microsoft, etc. |
Passed its peak in adoption |
|
Built-in security features |
Signalling is not standardised |
Certainly, many generic peer-to-peer web applications choose WebRTC as their toolset to develop with– and this will continue to be the case well into the future. But, there are two major reasons for the unquestionable dominance of WebRTC to wane a little into the future.
Mainly, the fact that it has peaked in adoption– meaning that next year and going into the foreseeable future there will be fewer applications made using WebRTC than there were before at its peak… And secondly, the advent of Communications Platforms as a Service (CPAAS).
WebRTC market analysis
The Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for seamless, real-time communication solutions across various sectors. In 2023, the market was valued at approximately USD 6 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.5% from 2024 to 2032, potentially reaching over USD 100 billion by 2032.
Let's explore the key drivers of WebRTC growth, market trends, and the current customer landscape.

Key drivers
The increasing demand for frictionless video and audio conferencing experiences is a key driver behind the growth of the web real-time communication (WebRTC) market. Other key market drivers include the following:
- The high adoption rate of WebRTC technology by enterprises.
- The rise in the use of videos for marketing, with more than 70% of business-to-consumer (B2C) marketers and 90% of business-to-business (B2B) marketers incorporating videos into their marketing strategies.
- The widespread adoption of smartphones and tablets has heightened the need for real-time communication tools that function effectively on mobile platforms, a demand that WebRTC addresses proficiently.
- WebRTC eliminates the necessity for additional plugins or software installations, offering a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- The webification of real-time communication.
- Growth in Internet connectivity and the development of Internet infrastructure in Asia-Pacific and Africa region.
Customer landscape
The WebRTC customer landscape is diverse, encompassing various industries and sectors. WebRTC technology has gained traction among businesses prioritising real-time communication and customer collaboration.
The demand for improved communication solutions in mission-critical sectors like banking, financial services, and healthcare drives the WebRTC market growth. As technology empowers various sectors with real-time communication and data handling needs, integrating efficient web scraping techniques becomes paramount. By leveraging web scraping proxy providers, businesses can automate data extraction processes efficiently, ensuring seamless access to vital web-based information while maintaining anonymity and overcoming common data acquisition barriers. This enhancement is pivotal for sectors driven by timely and accurate data analytics.
WebRTC market trends & predictions for 2025
The following trends and predictions highlight the ongoing evolution of WebRTC as it continues to shape the landscape of real-time communication in 2025.
Let's explore them below.
Integration with emerging technologies
The convergence of WebRTC with technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionise real-time communication. AI enhancements, including voice recognition, natural language processing, and sentiment analysis, are expected to significantly augment the capabilities and user experiences of WebRTC applications.
Adoption across small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
Advancements in mobile technology
The proliferation of smartphones and tablets has heightened the demand for seamless, instantaneous communication on these devices. WebRTC caters to this need by offering a standardised framework for embedding real-time communication features directly within mobile browsers, aligning with user expectations in a mobile-centric society.
Impact of remote work trends
The rise of remote work has accelerated the adoption of WebRTC solutions, which are essential for maintaining efficient communication and collaboration among distributed teams. This trend is expected to continue, further boosting the WebRTC market.
Increase in the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) practice
The integration of AI in WebRTC and the rapid increase in the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) practice are the key market trends for WebRTC.
BYOD encourages employees to use their personal devices in the workplace, with over one-third of employers worldwide providing devices and more than half promoting BYOD.
Unlocking the potential of WebRTC with Digital Samba
Digital Samba offers an end-to-end, GDPR-compliant, and encrypted solution for real-time communication. Our optimised WebRTC video API ensures low latency, scalability, and security. With Digital Samba, setting up audio or video streaming is effortless. It provides features like seamless integration with existing hardware and software, user authentication, encryption, and more.
Schedule a demo to experience the ease of streaming video with Digital Samba Video API today!
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

What is WebRTC: How It Works and Its Key Applications

A Comparison of WebSocket VS WebRTC


